
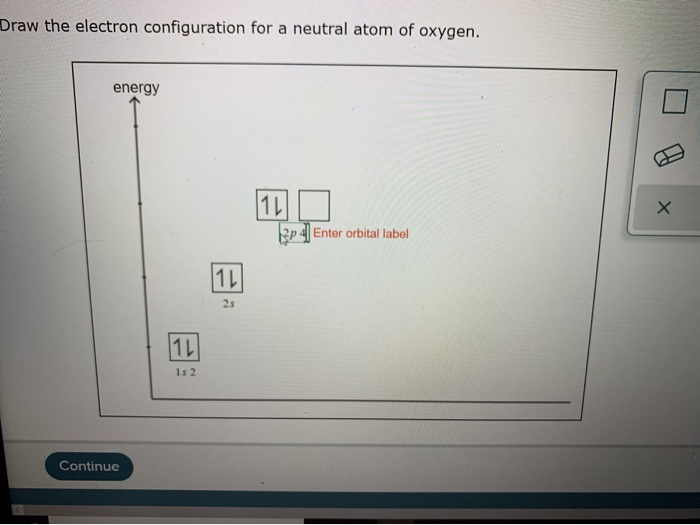
How can you tell if an atom is neutral A proton and an electron have an equal amount but an opposite type of charge. The mass number of an atom is calculated by adding together the number of protons and neutrons that are found within that atom, as shown below. Therefore, every atom of tungsten also contains 74 electrons. The mass number of the atom (M) is equal to the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. Since an atom must have an overall neutral charge, the number of protons and electrons found within an atom of an element must be equal. If a neutral atom has 10 protons, it must have 10 electrons. The number of electrons in a neutral atom is equal to the number of protons.

The atomic number is 6 since there are 6 protons. Luckily, one electron has the same charge (with opposite sign) as a proton. Its main advantage is the potential of scaling to. If a neutral atom has 2 protons, it must have 2 electrons. A neutral atom is an atom where the charges of the electrons and the protons balance. Neutral atoms trapped in optical lattices are a promising quantum-computing platform. If a neutral atom has 1 proton, it must have 1 electron.
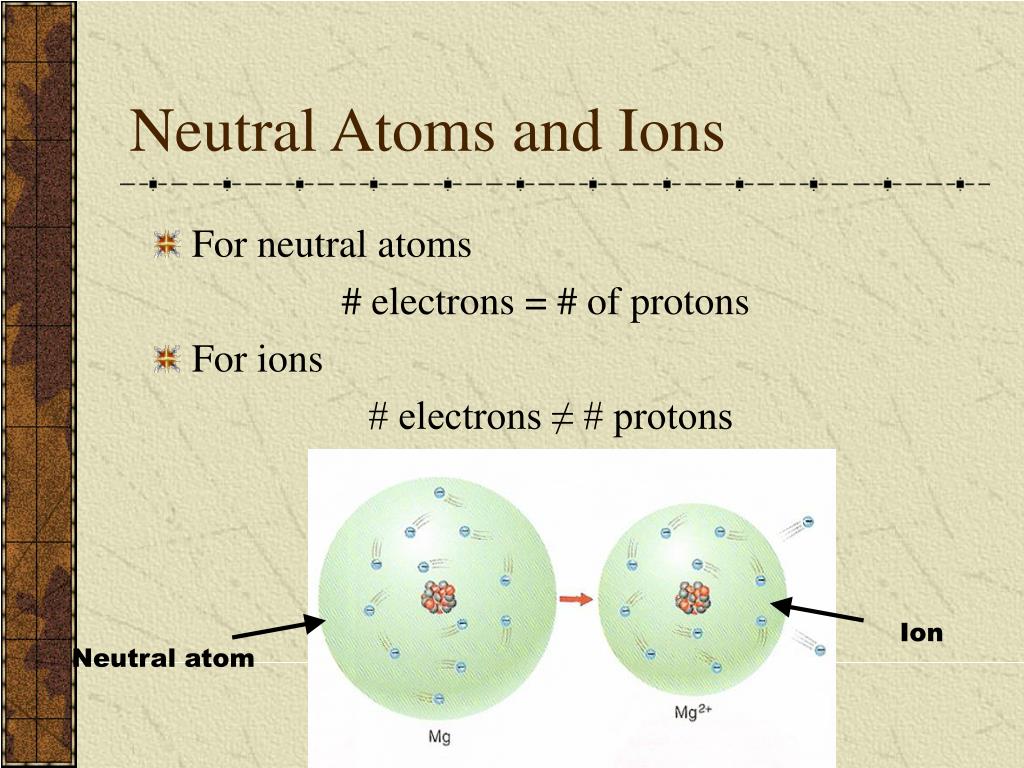
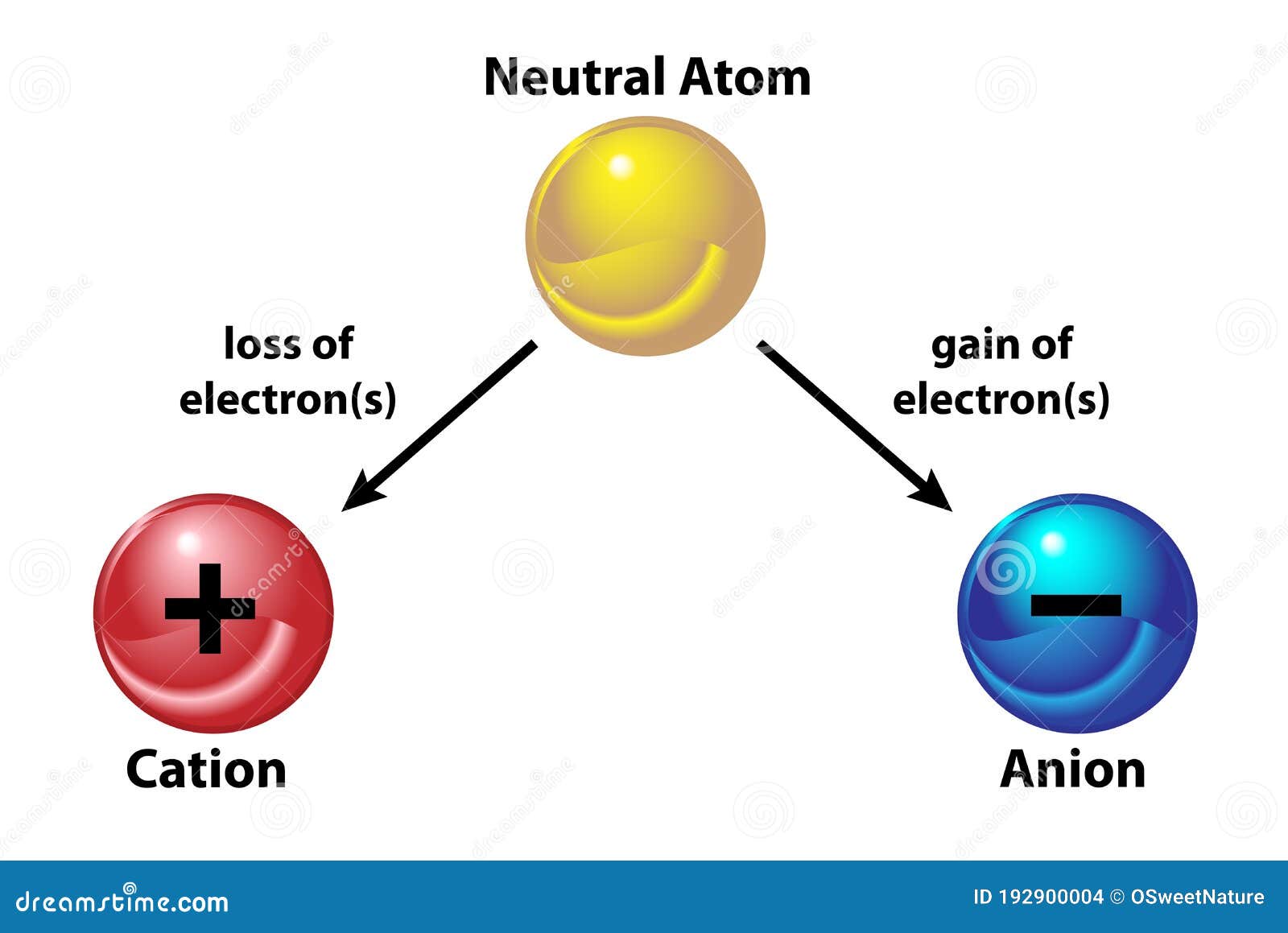
In other words, a neutral atom must have exactly one electron for every proton. This make them more immune to noise and means they can stay coherent, or in superposition, for a relatively long time. In addition, the fact that neutral atoms lack electric charge means they do not interact easily with other atoms. This means that the negative charge on an electron perfectly balances the positive charge on the proton. By comparison, scientists can pack neutral atoms closer together. Negative and positive charges of equal magnitude cancel each other out. Because its 2n shell is filled, it is energetically stable as a single atom and will rarely form chemical bonds with other atoms.\)) are useful, because, as you can see, the mass of a proton and the mass of a neutron are almost exactly \(1\) in this unit system. When the numbers of these subatomic particles are not equal, the atom is electrically charged and is called an ion. For instance, lithium ( Li \text Ne start text, N, e, end text ), on the other hand, has a total of ten electrons: two are in its innermost 1 s 1s 1 s 1, s orbital and eight fill the second shell-two each in the 2 s 2s 2 s 2, s and three p p p p orbitals, 1 s 2 1s^ 2 1 s 2 1, s, squared 2 s 2 2s^ 2 2 s 2 2, s, squared 2 p 6 2p^6 2 p 6 2, p, start superscript, 6, end superscript. Atoms are electrically neutral if they contain the same number of positively charged protons and negatively charged electrons. The framework site density of catalysts is estimated as 7.8 × 1018sites g1. This method allows us to deconvolute the framework sites and metal-based active sites.
Neutral atom software#
Elements in the second row of the periodic table place their electrons in the 2n shell as well as the 1n shell. Munich-based planqc, a quantum computing startup, announced on Friday, May 5 that it has been chosen by the German Aerospace Center (DLR) for an ambitious project to develop a scalable hardware and software platform for digital neutral-atom-based quantum computing. The site density of the single metal atom sites is estimated using the nitrite adsorption and stripping method. After the 1 s 1s 1 s 1, s orbital is filled, the second electron shell begins to fill, with electrons going first into the 2 s 2s 2 s 2, s orbital and then into the three p p p p orbitals.
Neutral atom plus#
The second electron shell, 2n, contains another spherical s s s s orbital plus three dumbbell-shaped p p p p orbitals, each of which can hold two electrons. Hydrogen and helium are the only two elements that have electrons exclusively in the 1 s 1s 1 s 1, s orbital in their neutral, non-charged, state. On the periodic table, hydrogen and helium are the only two elements in the first row, or period, which reflects that they only have electrons in their first shell. The difference between the neutron number and the atomic number is known as the neutron excess: D N Z A 2Z. Neutron number plus atomic number equals atomic mass number: N+ZA. This is written out as 1 s 2 1s^ 2 1 s 2 1, s, squared, referring to the two electrons of helium in the 1 s 1s 1 s 1, s orbital. The total number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is called the neutron number of the atom and is given the symbol N. Helium has two electrons, so it can completely fill the 1 s 1s 1 s 1, s orbital with its two electrons. This can be written out in a shorthand form called an electron configuration as 1 s 1 1s^ 1 1 s 1 1, s, start superscript, 1, end superscript, where the superscripted 1 refers to the one electron in the 1 s 1s 1 s 1, s orbital. Hydrogen has just one electron, so it has a single spot in the 1 s 1s 1 s 1, s orbital occupied. The 1 s 1s 1 s 1, s orbital is the closest orbital to the nucleus, and it fills with electrons first, before any other orbital. The first electron shell, 1n, corresponds to a single 1 s 1s 1 s 1, s orbital.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
